Home » Conditions » Skin & hair » Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma is a ‘small fat deposit’ that appears on the eyelids. The upper and/or lower eyelid may be affected. This subcutaneous lipid deposit is not dangerous to health but requires screening for possible abnormalities in the lipid profile.
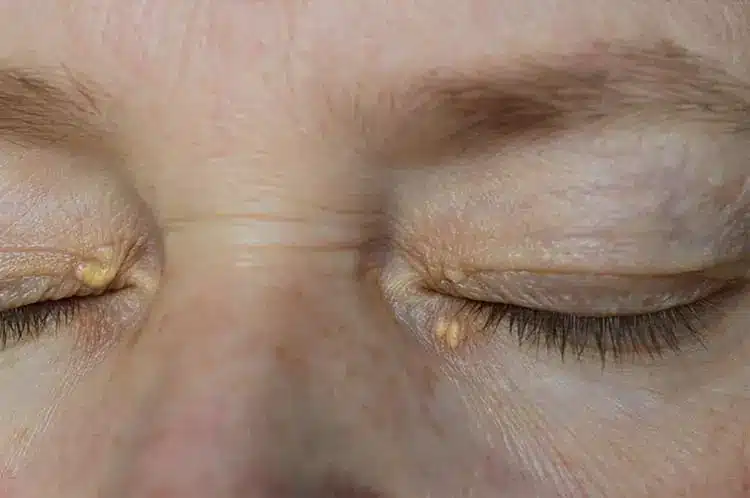
The appearance of xanthelasma may be :
In both cases, macrophages — cells responsible for eliminating foreign substances — capture molecules present in the body and become surrounded by lipid particles. These clusters then deposit on the eyelids, forming xanthelasma.
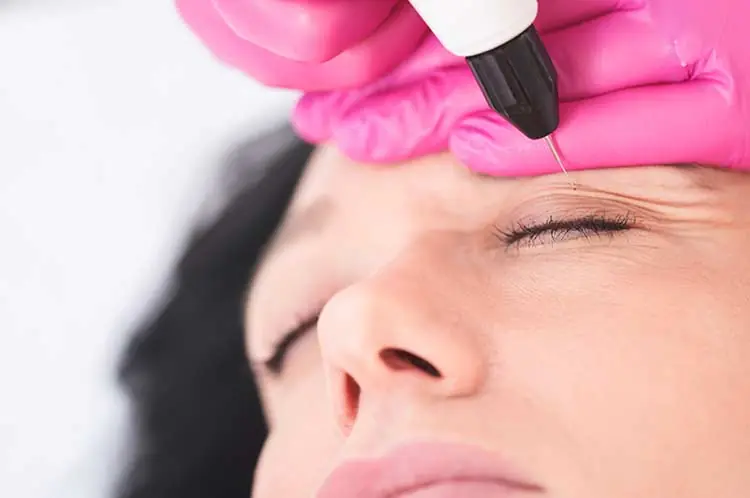
The treatment of xanthelasma addresses an aesthetic concern. Indeed, these lesions are not dangerous for health.
The investigation of a lipid profile abnormality is mandatory and must be managed in case of an increased cholesterol level.
Dr. Romano almost exclusively uses the electric scalpel for the removal of these lesions, which is much less traumatic than an ablative laser.
It is a kind of pen with a needle at the tip that selectively vaporizes the lesion.
Local anesthesia is performed, the treatment lasts about ten minutes.
For one week, the continuous application of a healing cream is recommended on the treated area.
The first few days, significant swelling may appear, depending on the patient’s skin tone and on the number and extent of the lesions.
The removal of xanthelasma exposes the underlying tissues, and in its place there will be a small hole that heals in one to four weeks. Once the skin has healed, it will have a pinkish color for two months.
The healing process lasts about six months.
The frequent side effect is a lighter or darker coloration than the skin at the treated area.
Recurrences are frequent, and no factor makes it possible to predict the recurrence time.
The treatment of xanthelasma is performed by Dr. Romano. The price starts at 300 CHF per session, with an adjustment depending on the number and size of the lesions to be treated. In the majority of cases, a single procedure is sufficient. If necessary, a touch-up can be performed at no cost, two months after the initial treatment. A personalized quote is provided during the initial consultation, based on the clinical evaluation.
Xanthoma is generally not serious, but it can be a sign of an excess of lipids in the blood (hyperlipidemia) or other metabolic disorders. Although it is benign, it is important to consult a doctor to identify its cause and assess the associated cardiovascular risk.
For xanthelasma, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist, a specialist in skin conditions. A general practitioner can also make an initial diagnosis and refer you to a specialist if necessary.
Certain creams containing trichloroacetic acid or retinoids can help reduce the size of xanthelasmas, but their effectiveness remains limited. These products must be used under medical supervision. However, the most effective treatments are generally dermatological procedures such as laser, cryotherapy or electrocoagulation.
Yes, makeup can temporarily conceal a xanthelasma. Using a high-coverage concealer and an appropriate foundation helps visually reduce the coloration. It is recommended to choose non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic products to avoid irritating the skin.
No, xanthelasma is painless. It appears as yellowish plaques on the eyelids, without causing pain. However, some patients may experience cosmetic discomfort.
Xanthelasma does not directly affect vision. However, if it becomes large, it can cause an aesthetic concern and, in rare cases, slightly hinder the opening or closing of the eyelids. Early treatment helps prevent any complication.