Home » Conditions » Skin & hair » Scars
The appearance of a scar results from a tissue repair process following a skin injury. As soon as the dermis is affected (burn, wound, pimples), the skin activates a physiological healing mechanism. Starting immediately after a trauma, this process aims to deeply repair the skin tissues and unfolds in several stages. Depending on the extent of the lesion, the total healing time can reach between 1 year and 1.5 years.
The healing phases are as follows :
• The coagulation phase : a blood clot forms after the bleeding and turns into a scab.
• The inflammatory phase or cleansing phase : leukocytes become active to clean the lesion and destroy any foreign bodies in the tissue. This phase is characterised by an inflammatory reaction that can cause redness and swelling (oedema) and an increase in temperature in the affected area.
• The proliferative phase : the dermis and the epidermis begin to rebuild. These neo-tissues are initially very imperfect.
• The remodelling phase : the structure and resistance of the scar improve, as does its appearance. Gradually, the scar becomes more supple.
The quality of healing varies depending on the size of the lesions, the quality of the skin and the person’s health condition. Indeed, the skin’s ability to regenerate depends on several factors (age, vascular diseases, nutritional deficiencies, smoking).
When abnormalities affect the healing process, visible and permanent scars form on the affected area. Several techniques exist in aesthetic-oriented medicine to reduce a scar.
Acne problems, surgical procedures, burns or even an accident can leave marks on the skin of the face or body. As reminders of these events, scars can be a source of psychological distress. To reduce or make a scar disappear, surgery is not necessarily required.
There are medical techniques that can remove a scar. These marks, sometimes difficult to accept, require personalised approaches to be effectively corrected. The available treatments are laser, hyaluronic acid injections, medium and deep peels.

Scars can appear in many situations :
• Severe acne : a frequent cause of atrophic scars.
• Surgery or medical procedures : incisions can leave visible marks.
• Accidents or injuries : cuts, burns or trauma.
• Stretch marks : the result of extreme tension on the skin (pregnancy, weight changes).
• Dermatological diseases : such as chickenpox or skin infections.
Because each scar is different, care must be personalised.

Healing is a complex process influenced by many internal and external factors.
• Age : younger patients generally heal faster thanks to higher collagen production, while more mature skin may heal more slowly.
• Genetics : some people are predisposed to developing hypertrophic or keloid scars.
• Skin type : darker skin is more prone to pigmented scars, while lighter skin may be more sensitive to prolonged redness.
• Location of the wound : areas that are highly solicited or under tension (knees, elbows) tend to heal less well.
• General health condition : chronic diseases (diabetes, vascular insufficiency) or deficiencies (zinc, vitamins A and C) can slow down healing.
• Infections : a local infection can worsen the scar by disrupting the skin regeneration process.
• Post-injury care : appropriate management (cleaning, hydration and protection) is necessary for optimal healing.
• Sun exposure : UV rays can cause hyperpigmentation of recent scars, making them more pronounced.
• Smoking : smoking reduces tissue oxygenation, thus delaying healing.
• Stress : chronic stress can disrupt the immune system and slow down the skin repair process.
Scars are classified according to their nature.
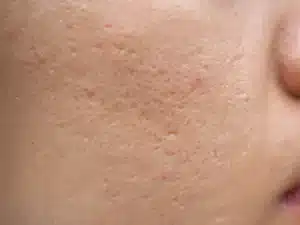
These are the most common scars. Due to a loss of dermal thickness at the site of the lesions, they appear as depressions on the skin surface. These scars do not regress naturally.
Three types of atrophic scars are distinguished, classified according to their shape, edges and depth : icepick scars, also called V-Shaped, boxcar scars, also called U-Shaped, and rolling scars, also called M-Shaped.
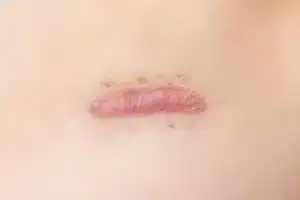
These raised lesions (less so than keloid scars) are red in color. Simple hypertrophic scars may disappear naturally within 12 to 18 months.
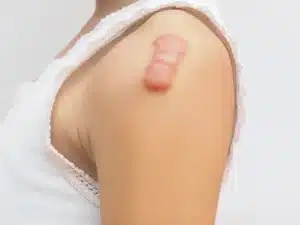
The keloid scar does not disappear spontaneously and is often associated with pain and/or itching. It appears as a raised lesion, slightly coloured between white, red, brown and pink. Its specific shape is due to an abnormal proliferation of skin tissue.

These marks refer to a healing pattern of superficial inflammatory lesions. While erythematous macules often disappear spontaneously within a few weeks without leaving marks, pigmented macules regress more slowly and to a variable extent.
In aesthetic-oriented medicine, several innovative techniques make it possible to reduce or eliminate a scar. These targeted treatments are adapted to each type of scar and skin.
Among the most effective solutions, the medium peel exfoliates the layers of the skin, thus stimulating cell renewal.
Ablative lasers, whether continuous or fractional, are powerful tools that regenerate skin tissues in depth, offering visible improvement of deep and long-standing scars.
For depressed scars, hyaluronic acid injections fill the skin depressions for an immediate, although temporary, effect. The treatment is personalised, and each technique is chosen according to the skin type, the nature of the scar and the patient’s expectations.

The fractional ablative laser reduces the scar by stimulating collagen production. It heats the skin tissues and creates tiny areas of ablation, thus promoting the regeneration of a denser and thicker dermis.
The number of sessions required varies between four and six.
The advantage of this technique is that the after-effects are quite mild (a social downtime of five days should be expected), but the improvement is less significant than that obtained with a medium or deep peel.
Pigmented scars are also faded.
The continuous ablative laser, ideal for old and deep scars, is used to perform a laser peeling. The goal is to remove the damaged layers of the skin to stimulate collagen production. This treatment, particularly effective on deep scars, allows a spectacular improvement reaching 80 % – 95 %.
The after-effects are marked by redness and scabs lasting 10 to 14 days.

The medium peel works by exfoliating the superficial and medium layers of the skin using specific solutions.
The medium peel is a TCA peel (trichloroacetic acid) using a 20–25 or 30 % concentration of TCA. Modified phenol is used to perform the deep peel.
By stimulating cellular regeneration, this treatment improves superficial and moderately deep scars, with an attenuation of up to 80 % depending on the skin type and the scar.
This technique is ideal for acne scars or pigmented scars.
The after-effects are identical to those of the laser peel.

The hyaluronic acid has two main indications :
• Correction of an isolated depressed scar : when the scar is not too fibrous, it can be filled thanks to the volumising properties of hyaluronic acid. In this case, Dr. Romano uses a moderately cross-linked acid.
• Dermal densification (improvement of the overall quality of the skin) : to thicken, tone and soften the skin, Dr. Romano uses the SkinBooster hyaluronic acid. A denser skin makes scars less visible.
During a prior informative consultation, Dr. Romano listens to the patient’s expectations, assesses their needs, analyses their skin and the type of scar, and advises them on possible treatments : laser or peel for scar.
A session lasts about 20 minutes, and the eyes are protected with ocular shields. The protocol includes 4 sessions spaced one month apart.
In case of a history of cold sores, a prophylactic antiviral treatment must be started the day before the session. One hour before the session, it is strongly recommended to apply the prescribed anaesthetic cream to the area to be treated. This makes the procedure painless.
After the session, a healing cream must be applied twice a day for at least 10 days.
Before performing the peel, a local anaesthesia is carried out to make the procedure completely painless. The area concerned is disinfected. Depending on the skin type and the intended goals, the number of passes and the application time of the peel vary. Immediately after its application, the peel causes intense redness and whitening of the skin (frost). This phenomenon is completely normal.
A skin preparation must begin 3 weeks before the peel, and Dr. Romano will indicate the cream most suitable for your skin. One month before the treatment, no self-tanner, essential oil, scrub or mask should be used.
On the day of the peel, makeup or even the application of a cream is forbidden.
After the session, a healing cream is applied to the treated area.
Post-peel after-effects are characterised by redness and slight swelling for about 48 hours, then the skin gradually darkens before peeling around the 7th day. Certain complications may occur : swelling, persistent redness, desquamation, exfoliation, bacterial or viral superinfection, acne flare-ups.
For the peel, several contraindications exist :
• Diabetes or severe insufficiencies such as renal or cardiac insufficiency.
• Pregnancy.
• Wearing a pacemaker or cardiac defibrillator.
• Isotretinoin treatment stopped less than a year ago or ongoing anti-acne treatment.
• Skin infection on the area to be treated.
• Recent aesthetic procedure (surgery, laser, dermabrasion).
• Dark phototypes.
• Contact skin allergies.
The first results are visible about one month after the treatment and are optimal between three and six months. This strongly depends on the treatment performed.
During the prior consultation, Dr. Romano explains that it is an improvement and not a complete disappearance of the scar ; the extent of the result depends on the type of scar and the patient’s skin.
An estimated improvement rate is also communicated during this consultation.
Scar treatments are intended for people who wish to :
• Reduce the visibility of scars.
• Improve skin quality and smooth surface irregularities.
• Reduce pigmented marks or persistent redness.
• Regain more even skin and boost self-confidence.
• Significant improvement in the appearance of the skin.
• Non-invasive or minimally invasive techniques.
• Natural stimulation of collagen synthesis for long-lasting results.
• Protocols adapted to each patient.
The cost of treating a scar varies depending on the technique used, the nature of the scar and the areas concerned. Dr. Romano welcomes you to her practice in Geneva for a diagnosis and a personalised quote.
Several approaches such as laser, peels or injections are offered : scar treatment using laser techniques or injections is based on a personalised approach adapted to the nature of the lesions and their location. Laser peeling is offered from 700 CHF per session, with a single session performed. Fractional ablative laser is offered from 500 CHF per session. Medium or deep peels, depending on the indication, are offered from 700 CHF, with only one session required. For certain indications, a hyaluronic acid injection may be recommended, at a cost of 600 CHF per syringe.
An abnormal scar is considered as such when it has an irregular shape, size abnormalities, or if it is painful. This includes hypertrophic scars (thick and red), keloid scars (extending beyond the edges of the wound), and atrophic scars (depressed). These scars may result from poor healing or a genetic predisposition.
Although no product can completely remove a scar, certain solutions support the healing process : silicone-based scar creams ; hyaluronic acid gels to improve skin quality ; retinoid creams to promote cell renewal ; plant oils (rosehip, vitamin E) to nourish and soften the skin.
To speed up the fading of scars : moisturise daily with suitable creams ; use silicone dressings to promote proper healing ; protect the scar from the sun to avoid pigmentation ; perform gentle massages to soften the scar tissue ; consult a doctor for targeted treatments such as laser.
There are different creams formulated to promote skin repair, smooth scars, soothe the skin or reduce hypertrophic and keloid scars. Some are enriched with repairing active ingredients, while others contain silicones or soothing agents that promote regeneration and softening of the skin. The choice of product depends on the type of scar, how old it is and the stage of healing.
A dermatologist and an aesthetic doctor are the specialists to consult to assess the scar and propose appropriate treatments. In some cases, a plastic surgeon may be required for more complex corrections.
Natural methods are not highly effective but are still useful : regularly apply rosehip oil or aloe vera to nourish and soften the skin ; use gentle scrubs to stimulate cell renewal ; massage with honey, which has healing properties.